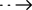It's CRE,It's CRO,It is CPE
- Categories:Newsroom
- Author:
- Origin:Medomics Medical
- Time of issue:2023-05-10
- Views:0
(Summary description)Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a serious global threat of growing concern to human, animal, and environment health. This is due to the emergence, spread, and persistence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria or “superbugs.”
It's CRE,It's CRO,It is CPE
(Summary description)Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a serious global threat of growing concern to human, animal, and environment health. This is due to the emergence, spread, and persistence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria or “superbugs.”
- Categories:Newsroom
- Author:
- Origin:Medomics Medical
- Time of issue:2023-05-10
- Views:0
Why AMR/MDR is Important
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a serious global threat of growing concern to human, animal, and environment health. This is due to the emergence, spread, and persistence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria or “superbugs.” Several fields of modern medicine depend on the availability of effective antibiotic drugs:infection therapeutic regimens/management, chemotherapy for cancer treatment/management, organ transplantation, hip replacement surgery, intensive care for pre-term newborns and many other procedures rely on prudent usages of antimicrobial agents. In fact, infections caused by MDR bacterial strains are among the main factors influencing morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing these procedures.
What is CPE/CRE/CRO
The spread of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) or known as carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) has become a major global public health threat and clinical concerns worldwide. Carbapenems have traditionally been used to treat infections caused by broad-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae and are still considered antibiotics to be used as a last resort. Certain bacterial isolates producing carbapenemases which are capable of hydrolyzing all carbapenems, cephalosporins, and beta-lactams, are the main cause of antimicrobial resistance to carbapenem antibiotics. Additionally, carbapenem-resistant organisms (CRO) describe resistant isolates also including non-fermented Gram-Negative bacteria, for example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, etc.. Most carbapenemase genes are located on plasmids or integrons which is easily transferred horizontally to other isolates, leading to rapidly spread worldwide. At present, the common carbapenemases mainly include KPC, IMP, NDM, VIM, and OXA-48 types.
Why CPE/CRE/CRO is Important
CPE/CRE/CRO is called a "superbug" because it is resistant to many new antibiotics, and the mortality rate of infected people is extremely high. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) accounted for more than 50%, according to recent studies. The CRKP detected might be only sensitive to tobramycin, amikacin and tigecycline, and is widely resistant to a variety of common clinical antibiotics including cephalosporins, carbapenems, quinolones and polymyxin B. Many studies have also demonstrated that CPE/CRE/CRO infected patients usually among older ages, COPD, long-term hospitalization history, admission to ICU, history of broad-spectrum antibiotic use, mechanical ventilation, and lower immunity population. These patients might have been hospitalized for a long time, accompanied by gastrointestinal infection and intestinal flora imbalance. It is speculated that the source of CPE/CRE/CRO infection may come from intestinal colonization. Related studies have shown that CPE/CRE/CRO colonization is an important risk factor, and up to 17% of patients with CPE/CRE/CRO colonization eventually transform into CRE/CRO infection. Early screening of high-risk asymptomatic patients (such as patients admitted to ICU, patients undergoing invasive medical procedures, and patients in CPE/CRE/CRO endemic areas) through anal swab/stool culture can detect high-risk patients with potential CPE/CRE/CRO infection as early as possible, thereby guiding clinical anti-infection treatment.
How CPE/CRE/CRO is Detected
Clinical manifestations of CPE/CRE/CRO infection may include fever, cough with sputum, etc. Inflammatory indicators such as WBC, CRP and PCT would increase. CPE/CRE/CRO isolates from specimens of infected sites should be tested with antibiotics susceptibility testing results. CPE/CRE/CRO usually manifests as MDR or even extensive drug resistance (XDR). Detection of carbapenemase mainly includes polymerase chain reaction (PCR), modified Hodge test (MHT), Carba NP test, modified carbapenemase inactivation test (mCIM), ethylene-glycol amino-tetra-acetic acid carbapenem inactivation test (eCIM), metallo-β-lactamase test with clavulanic acid synergy test and EDTA enhanced test, and more recent development of lateral flow immunoassay rapid POCT tests. Recent newly developed Lateral Flow Rapid POCT tests can definitely expedite the determination of potential CRO/CRO isolates within 15 mins.
 What are CPE/CRE/CRO Potential Treatment Regimens
What are CPE/CRE/CRO Potential Treatment Regimens
Due to the limited availability of therapeutic drugs for CRE/CRO, amikacin, tigecycline, and recently approved ceftazidime/avibactam still have some antibacterial activity. Polymyxins have also re-emerged becoming the "last line of defense" for CPE/CRE/CRO infection. In severe CPE/CRE/CRO infections, polymyxins are often combined with tigecycline, meropenem, amikacin, or fosfomycin to exert synergistic antibacterial effects. In addition, some new treatment methods are also being actively developed, such as phage therapy, immunotherapy and antimicrobial peptide therapy.
Conclusions
In conclusion, when faced with suspected CPE/CRE/CRO infection clinically, antibiotics susceptibility testing results should be performed as soon as possible to clarify the drug resistance mechanisms, in order to initiate proper therapeutic regimes. Recent new development of Lateral Flow Rapid POCT tests can definitely expedite the determination of potential CRO/CRO isolates rapidly. In addition, preventive measures are more important. Avoiding the risk factors of CPE/CRE/CRO colonization and infection, limiting the abuse of antibiotics, early screening of CPE/CRE/CRO colonization using POCT rapid tests, and timely removal of the source of infection are critical to controlling the spread of CPE/CRE/CRO infection.
Available area: European Union
Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis [published correction appears in Lancet. 2022 Oct 1;400(10358):1102]. Lancet. 2022;399(10325):629-655.
Bharadwa jR,Robinson ML,Balasubramanian U,etal.Drugresistant Enterobacteriaceae colonization is associated with healthcare utilization and antimicrobial use among inpatients in Pune,India[J].BMCInfectDis,2018,18(1):504
Kelly A M, Mathema B, Larson E L. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in the community: a scoping review. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2017, 50(2): 127-134.
Logan Latania K,Weinstein Robert A,The Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: The Impact and Evolution of a Global Menace[J].J. Infect. Dis., 2017, 215: S28-S36.
Wang Q, Wang X, Wang J, et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: data from a longitudinal large-scale CRE study in China (2012-2016). Clin Infect Dis, 2018, 67: S196-s205.
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
- Email Us overseas@medomics-dx.com
- Call Us +86-025-58601060
- COVID-19 Solution
- Top
Contact Us
Phone: (+86) 025 - 58601060
E-mail: overseas@medomics-dx.com
Address:Building 01, Phase 6, No.71, Xinghui Road, Jiangbei New Area, Nanjing
- Email Us
- COVID-19 Solution
- Call Us (+86) 025 - 58601060
- top
Jiangsu Medomics Medical Technology Co,Ltd Powered By www.300.cn