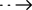Development of a cost-effective rapid detection of carbapenem-resistance Gram-negative bacteria laboratory workflow
- Categories:Newsroom
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2024-02-07
- Views:0
(Summary description)Spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) has become a major global public health threat and clinical concerns worldwide.
Development of a cost-effective rapid detection of carbapenem-resistance Gram-negative bacteria laboratory workflow
(Summary description)Spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) has become a major global public health threat and clinical concerns worldwide.
- Categories:Newsroom
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2024-02-07
- Views:0
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
- Email Us overseas@medomics-dx.com
- Call Us +86-025-58601060
- COVID-19 Solution
- Top
Contact Us
Phone: (+86) 025 - 58601060
E-mail: overseas@medomics-dx.com
Address:Building 01, Phase 6, No.71, Xinghui Road, Jiangbei New Area, Nanjing
- Email Us
- COVID-19 Solution
- Call Us (+86) 025 - 58601060
- top
Jiangsu Medomics Medical Technology Co,Ltd Powered By www.300.cn